What is Energy Efficiency?
In a day and age where more and more people want to reduce their carbon footprint, energy efficiency has become a popular catchphrase or buzzword that is so broad that it is sometimes a bit ambiguous.
What is energy efficiency? Is there a specific definition?
This term can have many different meanings depending on how and when it is used. Consumers can define ‘energy efficiency’ as a means of maximizing energy usage while minimizing individual carbon footprints. Basically, energy efficiency is getting the most bang for your energy buck by using the least amount of energy as necessary. Energy efficiency is in many respects the embodiment of ‘waste not, want not.’
Read on to learn more about energy efficiency, the benefits of being energy efficient, why being energy efficient is important, and what is not energy efficient:
Energy Efficiency Definition 101
The definition of energy efficiency, in its simplest form, means employing less energy to fulfill the same service. For example, a compact fluorescent light bulb is more energy efficient than a regular incandescent light bulb because the former requires less electrical energy to generate the same amount of light as the latter. LED bulbs also are incredibly energy efficient.
Being energy efficient or using energy efficient products also means that you are saving money by using less energy, without sacrificing quality or comfort.
Properly insulating a house, for instance, means that a lower amount of energy is needed to heat or cool the house properly, and using fluorescent lights rather than incandescent lights not only will provide the same lighting intensity, but also will end up costing less on the monthly electricity bill. Ultimately, this helps people lessen their greenhouse gas emissions and therefore safeguard the environment.
Adding insulation around water pipes helps keep heat from escaping, and allows the water to stay at the optimum temperature without using additional electric or gas resources. Pipes without insulation are less energy efficient as additional electricity or gas needs to be used to replace the heat that escapes from the exposed pipe.
In addition to insulation and fluorescent light bulbs, energy-efficient appliances—like fridges, dryers, washers, ovens, freezers, stoves, and dishwashers—can help to reduce energy consumption. Consumers who want to simplify the process of finding energy efficient appliances need to look for the Energy Star mark. Those who invest in Energy Star products also may be able to save additional money thanks to rebates; the Energy Star program provides a search query page to help consumers find any qualified rebates with Energy Star products.
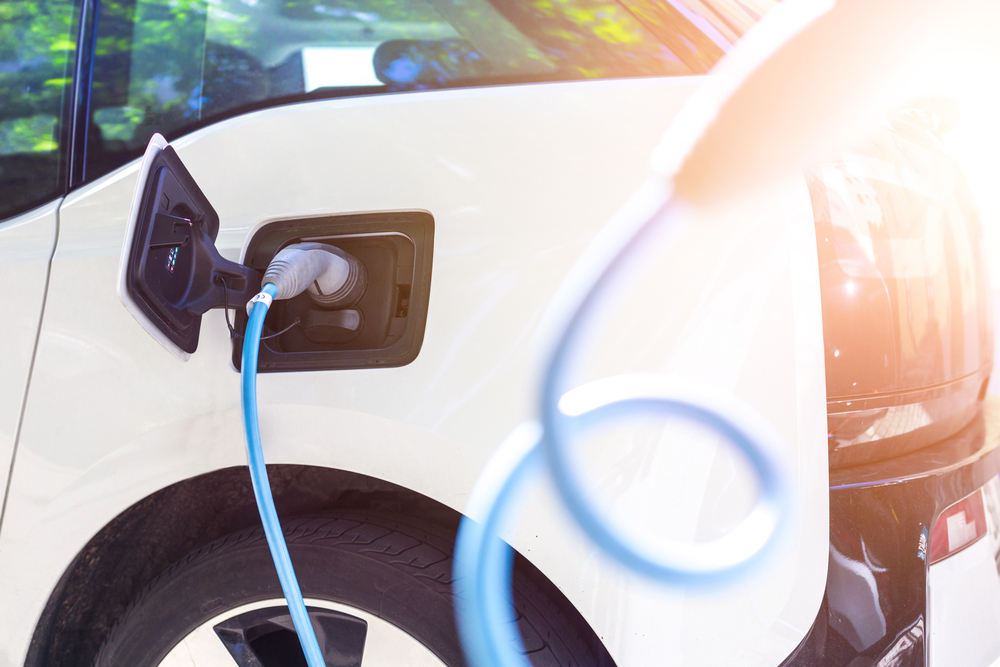

Energy Efficiency on the Road
Energy efficiency isn’t just limited to household appliances and fixtures. Another prime example of this concept would be energy efficient vehicles. Some engines are built to drive hundreds of miles on a single tank of gas, while a sports-car might only get a few dozen miles out of a full tank of gas. One vehicle consumes more energy at a faster rate than the other vehicle which performs essentially the same function, without wasting as much energy.
Some vehicles drive on electric, which saves fossil fuel. Others drive on diesel, instead of standard gasoline. Hybrid vehicles combine electric and gas as power sources. Finding the best energy efficient vehicle is all in the math. Consumers should look at how many miles per gallon (mpg) a vehicle can clock on the highway and within the city (think side streets and stop and go traffic on smaller roads). Highway driving optimizes gas consumption, while driving a lot of ‘city’ miles is less gas efficient.

Energy Efficiency through Daily Habits
While energy efficient appliances, bulbs and vehicles can save money and decrease our mark on the planet, our habits also play a large role in energy consumption.
Changing our actions can help lower our monthly energy bills and waste less precious resources. How do you become energy efficient through action? It’s easier than you think!
Recycle
Tossing that glass bottle, paper product or aluminum can in the garbage sends that waste to the landfill where it’s left to decompose. Many items can have a second life through recycling, and this helps save landfill space and decreases the need for the production of more materials.
Paper products, glass and aluminum are materials that have a second life. Your waste disposal company may even provide pick-up for recyclables. If not, research where to drop off your items. When recycling, create separate bins for each material. The Glass Packaging Institute recommends sorting colored glass by hue (e.g. keep those root beer bottles separate!).
Recycling aluminum cans may even come with some extra pocket change depending on your home state!
Decrease Water Waste
A leaking pipe or fixture wastes water, and a leak also could cause damage. Running the tap unnecessarily will run up the bill, too.
Once a month, check out all the faucets and pipes in the home. Look for any drips and leaks and call a plumber if you notice something amiss. This may help you decrease water waste and proactively catch any leak that could lead to damage down the road.
Your habits also help reduce waste. Turn off the water when you’re brushing your teeth or soaping up your hands. That tap doesn’t need to flow unnecessarily.
Limit the time spent in the shower, too. Yes, a hot shower is relaxing. However, a long hot shower uses up electricity or gas (for the heat) and water. To limit shower time, set a timer and stick to it!
Turn off the Lights
Are those bulbs burning the midnight oil? Turn them off! Every time you leave a room, flip the switch to turn off the lights.
Using power strips and outlets controlled by IoT (the Internet of Things) can help you remember to switch off those lights, too. Smart plugs and power strips are controlled by a phone or tablet and typically can be turned off remotely. Think you left the lights on? Check your phone!
The cheapest form of light, though, is the sun. If the day isn’t too hot, open up the curtains and let the sun in. You’ll brighten the room…and maybe your mood, too. Plus, the sun is free!
Carpool
Don’t have the money to invest in a hybrid or electric vehicle? Save money and energy by carpooling! This is a great option for those who live close by co-workers or fellow students.
When three or four people share the gas money, everyone wins. Carpooling also decreases the number of vehicles on the road, which may mean a little less pollution.
Grab a Bike
Those who live in a small town or a city or town that’s bike-friendly should take advantage of the opportunity. Bikes are extremely energy efficient, as they use no fossil fuels or electricity. A bicycle is powered by human strength.
Not only does this mean energy savings, but you’ll also get a nice workout! Always follow safety protocol when biking—wear a helmet and reflective clothing and obey the traffic laws.
Remember that Less is More
How many loads of dishes or laundry do you wash each week? Are all those loads filled to capacity? When you wash a small load of clothing or fill the dishwasher with only a few dishes, you’re wasting money and energy.
Yes, there are times when an item has to be washed immediately—and perhaps separately. When possible, adjust the water level or the wash cycle to optimize energy. Otherwise only wash full loads of dishes and laundry.
Call Your Utility Company
Some electric providers may offer rebates or special programs. Check with your provider to find out ways to save and to inquire about any special programs or rebates.
What is energy efficiency? This buzzword can have many meanings, depending on the context. Generally, though, energy efficiency is all about maximizing savings by minimizing energy consumption. Energy efficiency is all about ‘waste not, want not’ and a less is more approach to living.
Appliances and light bulbs can provide energy saving features. Vehicles can optimizes gas consumption or provide energy efficiency through electrical power versus the use of fossil fuels. Our daily habits also can help maximize energy efficiency by changing the way we use our resources and ensuring that light, heat and water aren’t being wasted.